istio traffic: 通过 service entry 访问虚拟机上的服务
by 伊布
本文基于istio 1.10版本。
service entry
istio默认是使用k8s作为注册中心,使用k8s的svc dns作为注册发现的机制。
在实际的生产环境下,可能用户的服务并不是部署在k8s上,而是在传统的容器中,针对这些服务,如何进行治理,是istio需要解决的问题。
istio给出的答案是 service entry。
ServiceEntry可以在Istio的内部服务注册表中添加额外的条目,这样网格中自动发现的服务就可以访问/路由到这些手动指定的服务。
一个服务条目描述了一个服务的属性(DNS名称、VIP、端口、协议、端点)。这些服务可以是mesh以外的服务(如Web API),也可以是不属于平台服务注册表的Mesh内部服务(如访问Kubernetes服务的一组虚拟机)。此外,服务条目的端点也可以通过使用workloadSelector字段动态选择。这些端点可以是使用WorkloadEntry对象声明的虚拟机工作负载或Kubernetes pods。
在单一服务下同时选择pod和VM的能力允许将服务从VM迁移到Kubernetes,而不必改变与服务相关的现有DNS名称。
访问集群外的服务
如下,将集群外的一台虚拟机上部署的nginx,集成到服务网格中,供网格中的客户端进行访问。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: nginx-x
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
hosts:
- xxx.example.com
location: MESH_INTERNAL
ports:
- name: http
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
resolution: STATIC
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: hello2-deploy
选择的workload entry
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: WorkloadEntry
metadata:
name: vm204
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
address: 192.168.0.204
labels:
app: hello2-deploy
class: vm
version: v1
域名解析
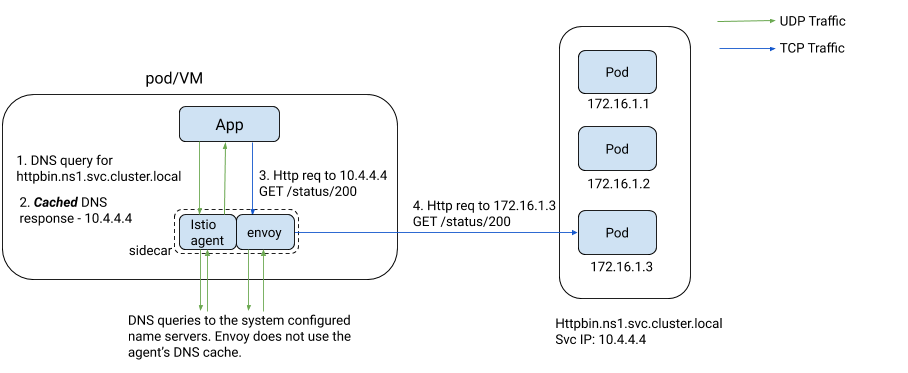
istio 默认不会自动解析service entry的域名,所以需要在客户端pod上手动配置其/etc/hosts文件,增加hosts记录 1.1.1.1 xxx.example.com,其中地址可以随意指定,目的是完成域名解析后,请求报文会被iptables劫持给envoy,由envoy基于hosts进行转发。
这里有一个疑问,不是说envoy接管了所有流量吗?为什么DNS解析的没有通过envoy解析呢?默认istio只是劫持了tcp流量,而DNS默认是通过udp发送的,所以不会经过envoy处理。
istio(1.10版本)支持了dns流量的劫持,会将DNS请求劫持给pilot-agent。注意,1.10之前的版本,会将DNS请求劫持给envoy,但后面发现不是很稳定,所以从1.10开始是劫持给了pilot-agent,由pilot-agent为service entry的域名分配ip地址。
开启方式可以是在configmap istio中增加如下的配置。
proxyMetadata:
# Enable basic DNS proxying
ISTIO_META_DNS_CAPTURE: "true"
# Enable automatic address allocation, optional
ISTIO_META_DNS_AUTO_ALLOCATE: "true"
开启后,在istio-demo下服务网格内的Pod,可以通过域名 xxx.example.com 访问虚拟机192.168.0.204上的nginx服务。
从实现上来看,iptables会将DNS请求劫持给pilot-agent。
# nsenter -t 29074 -n iptables-save|grep 53
-A OUTPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m owner --uid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A OUTPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m owner --gid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A OUTPUT -d 10.96.0.10/32 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 15053
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT ! -d 127.0.0.1/32 -o lo -p tcp -m tcp ! --dport 53 -m owner --uid-owner 1337 -j ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -o lo -p tcp -m tcp ! --dport 53 -m owner ! --uid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -o lo -p tcp -m tcp ! --dport 53 -m owner ! --gid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -d 10.96.0.10/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 15053
# nsenter -t 29074 -n netstat -antup |grep -i 15053
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:15053 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 29222/pilot-agent
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:15053 0.0.0.0:* 29222/pilot-agent
pilot-agent会从一个E类地址(240.240.0.0/16)为service entry分配IP地址,例如本例里分配的地址是 240.240.0.1 。
[root@debian-77dc9c5f4f-q2hb2 /]# ping xxx.example.com
PING xxx.example.com (240.240.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data
注意,只有满足这三种情况才会为service entry自动分配IP地址。
- the service has resolution set to static/dns. We cannot allocate for NONE because we will not know the original DST IP that the application requested.
- the address is not set (0.0.0.0)
- the hostname is not a wildcard
对于多副本的istiod部署情况下,由于ip分配算法是固定的,所以最终各个service entry的地址是一致的。
func autoAllocateIPs(services []*model.Service) []*model.Service {
maxIPs := 255 * 255 // are we going to exceeed this limit by processing 64K services?
x := 0
for _, svc := range services {
if svc.Address == constants.UnspecifiedIP && !svc.Hostname.IsWildCarded() &&
svc.Resolution != model.Passthrough {
x++
if x%255 == 0 {
x++
}
if x >= maxIPs {
log.Errorf("out of IPs to allocate for service entries")
return services
}
thirdOctet := x / 255
fourthOctet := x % 255
svc.AutoAllocatedAddress = fmt.Sprintf("240.240.%d.%d", thirdOctet, fourthOctet)
}
}
return services
}
评:目前看,istio通过内置dns server,一方面解决了service entry没有域名解析的问题,另一方面也解决了kube-dns的负载压力(缓存)。istio的IP分配策略,与腾讯云TSF不一样:TSF为所有的service均分配了相同的地址。TSF这么做的主要原因是,其主要支持基于http的微服务(Spring Cloud),所以分配相同的地址没有什么问题。但istio可能还要支持TCP类型的服务,对于这种服务就需要其IP地址不同,否则envoy无法区分流量。
域名可以解析后,从服务网格的容器作为客户端进行请求,可以访问到虚拟机上的服务(虚拟机上的nginx主页改为了Welcome to nginx on vm204!)。
[root@debian-77dc9c5f4f-q2hb2 /]# curl xxx.example.com
Welcome to nginx on vm204!
从VM迁移到k8s容器
前面我们基于label app: hello2-deploy,将workload entry vm204加入到了service entry nginx-x,实现了将外部虚拟机上的服务,接入到服务网格
那么如何将服务迁移到istio上呢?service entry除了可以通过label来选择workload entry,也可以通过label来选择pod。
如下,部署Deployment hello2-deploy,其pod的label为 app: hello2-deploy。注意这里关闭了改服务的sidecar注入,仅作为一个简单的nginx服务。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: hello2-deploy
name: hello2-deploy
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello2-deploy
class: docker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello2-deploy
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
pod创建后,仍然从服务网格的容器作为客户端发起请求,可以看到,多次请求响应的内容是不同的(交替返回为vm204的修改页面和nginx默认页面),说明是service entry可以路由到workload entry和pod。
流量治理
经过上面的操作,实现了将应用部署到了虚拟机和容器,那么一段时间后,需要将流量从虚拟机迁移到容器,这时就需要用到istio的流量治理。
创建hosts对应的vs和dr。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
namespace: istio-demo
name: hello2-dr
spec:
host: xxx.example.com
subsets:
- name: vm
labels:
class: vm
- name: docker
labels:
class: docker
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
namespace: istio-demo
name: hello2-vs
spec:
hosts:
- xxx.example.com
http:
- name: http-hello-route
route:
- destination:
host: xxx.example.com
subset: vm
weight: 0
- destination:
host: xxx.example.com
subset: docker
weight: 100
注意,istio在这里针对service entry的hosts是有一些隐含的逻辑的。如果 service entry 的hosts为 xxx,并且 virtual server的hosts也设置为 xxx,这样配置会不生效,查看pod的proxy-config,会发现有2个DOMAIN:xxx和 xxx.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local,这样VS是配置在为virtual service自动生成的DOMAIN xxx.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local上的,这样也就不生效了。
# istioctl proxy-config route debian-77dc9c5f4f-wxw6x.istio-demo --name 80
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
80 xxx.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local /* hello2-vs.istio-demo
80 xxx /*
所以,在上面的示例中,需要将hosts设置为 xxx.example.com,这样VS是配置在DOMAIN xxx.example.com上的。如上,设置VS将流量全部到给subset docker,从服务网格的客户端发送请求,可以验证流量都导给了容器上的标准nginx。
# istioctl proxy-config route debian-77dc9c5f4f-wxw6x --name 80
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
80 xxx.example.com /* hello2-vs.istio-demo
问题与缺陷
- 只能进行流量控制,不能配置故障注入、超时、限速等等。
- WorkloadEntry的引入解决了从网格内的POD向VM中的应用请求的流量管理。但是反方向的请求单靠WorkloadEntry是不能解决的,因为VM中的应用无法找到网格内的POD。到目前为止,我们的VM还没有真正意义地实现网格化,只有完全实现网格化,VM内才能为应用提供sidecar,进而通过POD对应的service,将VM应用的请求路由到POD。
Ref:
Subscribe via RSS
